
The cadmium content in the soil and water has increased due to the use of contaminated sludge and phosphate fertilizers and industrial water discharge. As a result, cadmium enters the food chain and drinking water.
Cadmium is a silver-gray transition metal with a relatively low boiling point. Cadmium ores are quite rare. Cadmium is almost always found in combination with zinc sulfide. It is therefore a by-product of zinc mining, and also occurs as a by-product of lead and copper mining. Cadmium is classified under the heavy metals and is in the periodic table with symbol Cd and atomic number 48.
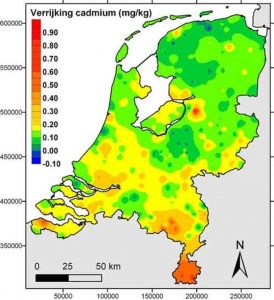
The WHO guidelines for drinking water quality stipulate that the concentration of cadmium in drinking water may not exceed 5.0 μg (micrograms) per liter. This really is the absolute maximum: the aim is to have no cadmium in drinking water at all. The European Food Safety Authority does not set a tolerable intake at all; cadmium is so toxic that the intake must be As Low As Reasonable Achievable (ALARA). Cadmium occurs naturally in the soil in low concentrations. Pollution of factories and emissions from zinc smelters and incinerators can further pollute the soil. Particularly in the south of the Netherlands and in some areas in Belgium, there is a lot of cadmium pollution. The recycling of batteries also releases quite a lot of cadmium.
Cadmium is highly toxic and has no function in the body. Even in low amounts, exposure can lead to symptoms such as:
Cadmium poisoning causes severe pain in the spine and joints, which is why it is sometimes called “Itai-Itai disease” (pain-pain disease) in Japan.
Exposure to low amounts of cadmium do not cause direct health problems, but due to accumulation, it disrupts kidney function in the long term and makes bones more brittle (osteoporosis). Long-term exposure to cadmium has also been linked to lung cancer. The International Agency for Research on Cancer classifies cadmium as “carcinogenic to humans”.
It is important to limit cadmium intake as much as possible. Do you live in areas with high cadmium concentrations? In that case, limit eating crops from your own region, especially leafy vegetables. Also do not use well or rain water. You can filter your tap water with ZeroWater to lower the cadmium concentration. Cigarettes also contain cadmium.
Yes, ZeroWater filters 97% cadmium from the tap water. The Premium 5-stage Ionization Changer Filtration System removes more impurities than the standard 2-stage filters. During the test, ZeroWater had 150 liters of filtered water (double the prescribed use) tested by an independently certified external laboratory. The test results are based on the NSF/ANSI test protocol of flow-through equipment for contaminants listed under the national primary drinking water standards.